Blockchain Essentials
Introduction and Overview of Blockchain as a Technology
Updated: 23 December 2025
Based on this Cognitive Class Course
Discover Blockchain
The Business Backdrop
Businesses are always operating with external organizations and markets. These business networks are fundamental to the operation of blockchain in this environment
These networks consist of transferring of different types of assets
- Tangible
- Intangible
- Cash
Ledgers are the key to recording the flow of assets through an organisational network, and these flows are governed by contracts which can be simple or complex
At a very high level Blockchain is a distributed ledger with a shared set of business processes across the network
The Problem Area
Every member of the business network has their own copy of the ledger, and this is updated each time an asset flows through the network, this system is inefficient, expensive, and vulnerable to mistakes or even fraud
By utilising Blockchain, each member utilises a shared ledger, but we just specify which users are able to see which specific transactions are relevant to them
When we use this we end up with
- Consensus
- Provenance
- Immutability
- Finality
Based on this we have a single source of truth for all parties and transactions within the network
Requirements in a Business Environment
Blockchain in a business environment requires four main components
- Shared Ledger
- Smart Contract
- Privacy
- Trust
Shared Ledger
Each participant has their own copy which is shared between them, this is based on permission and control. This becomes the shared system within the network
Smart contracts
Encoded version of business contracts. These are verifiable, and signed. Once these are distributed the contract will execute one the conditions are met.
Privacy
Participants need confidentiality within the blockchain, as well as a system in which transactions must be authenticated and immutable
Trust
Selected members endorse or validate transactions, once these are endorsed they are added to the blockchain. This gives us a verifiable audit trail, transactions cannot be modified in any way once they have been added
Benefits of Blockchain
- Save Time
- Remove Costs
- Reduce Risk
- Increase Trust
Asset Transfer Lab
Set up Hyperledger Composer Playground
Go to the Composer Playground
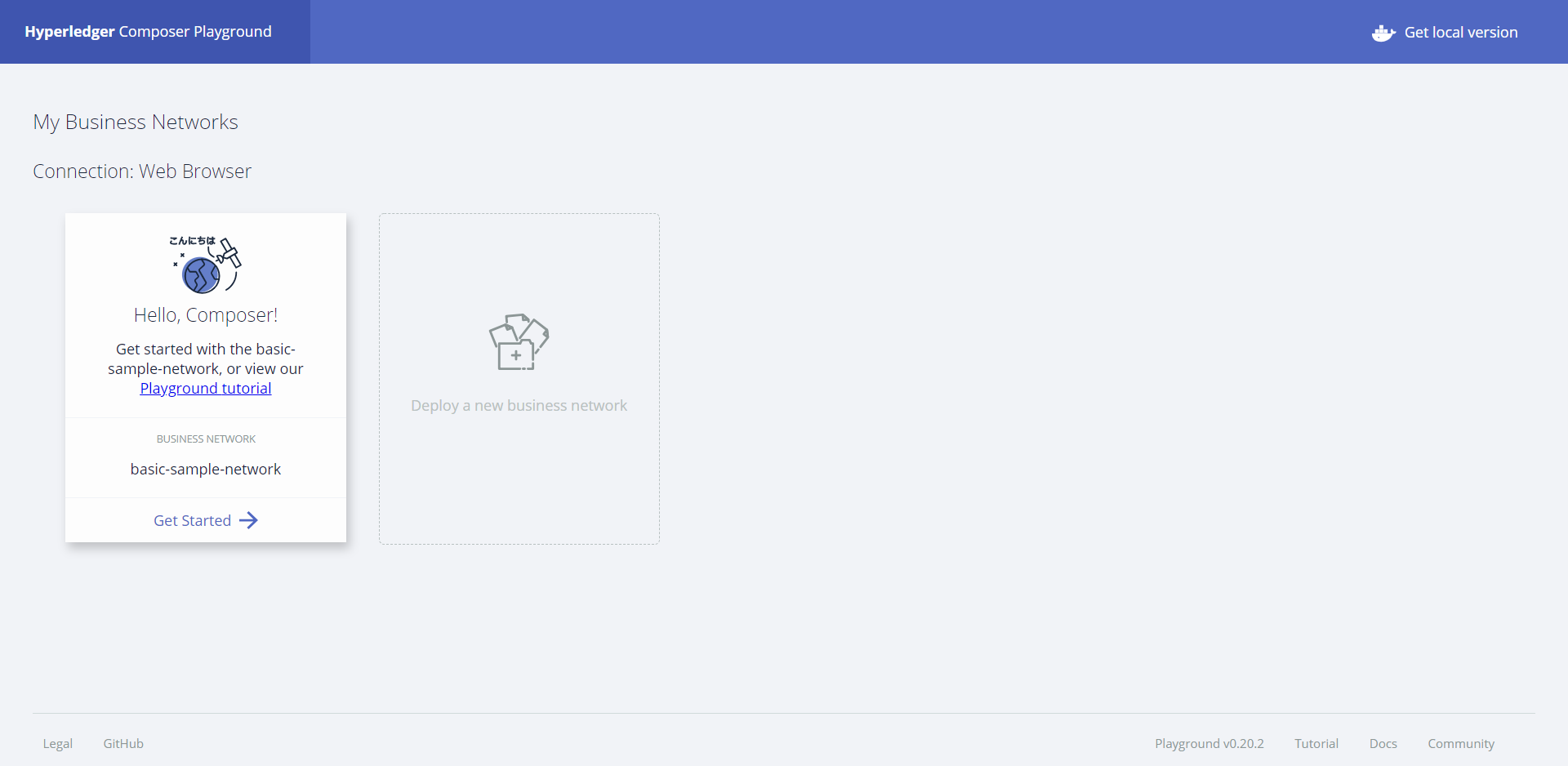
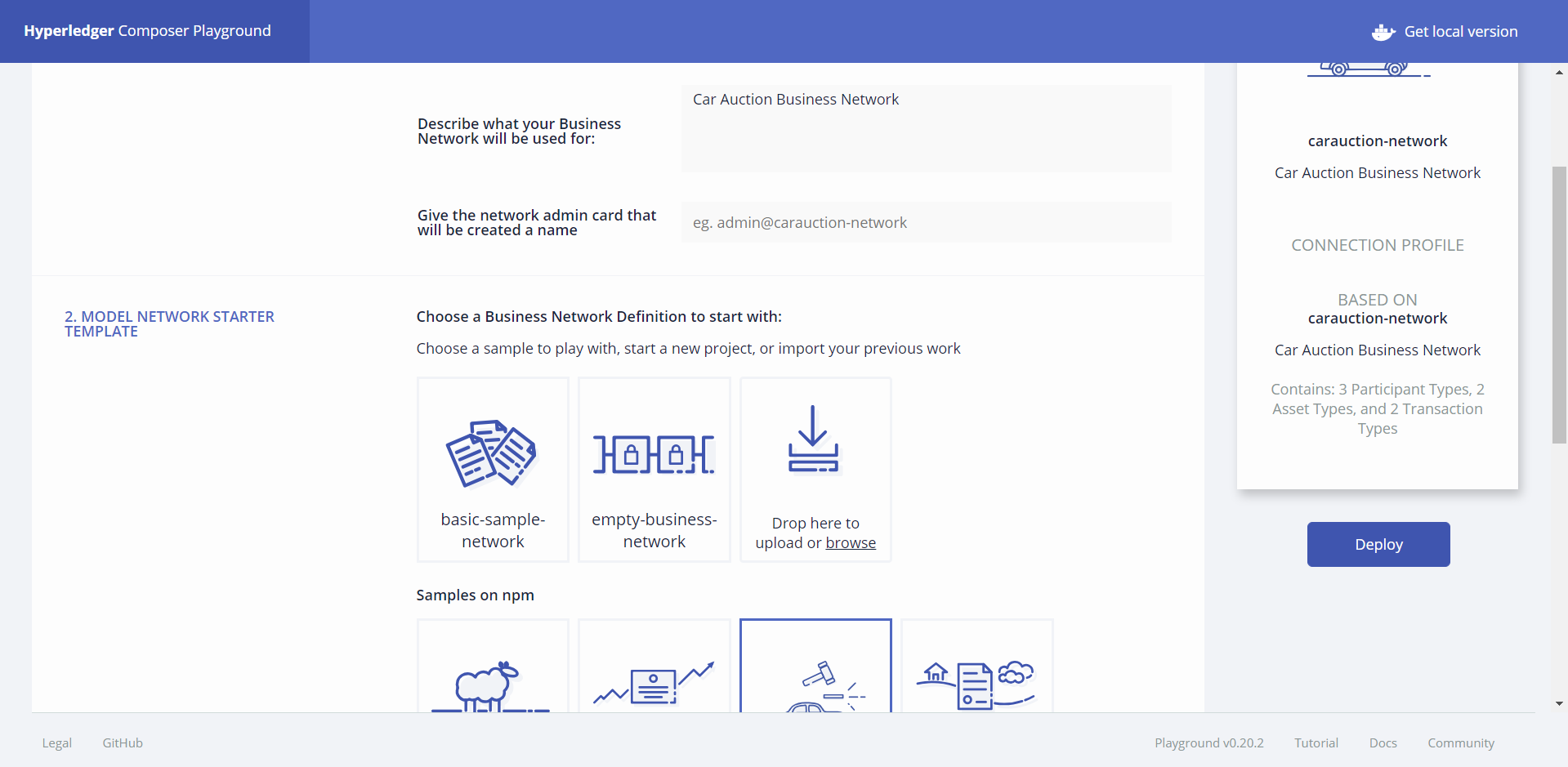
Then Create a Business Network
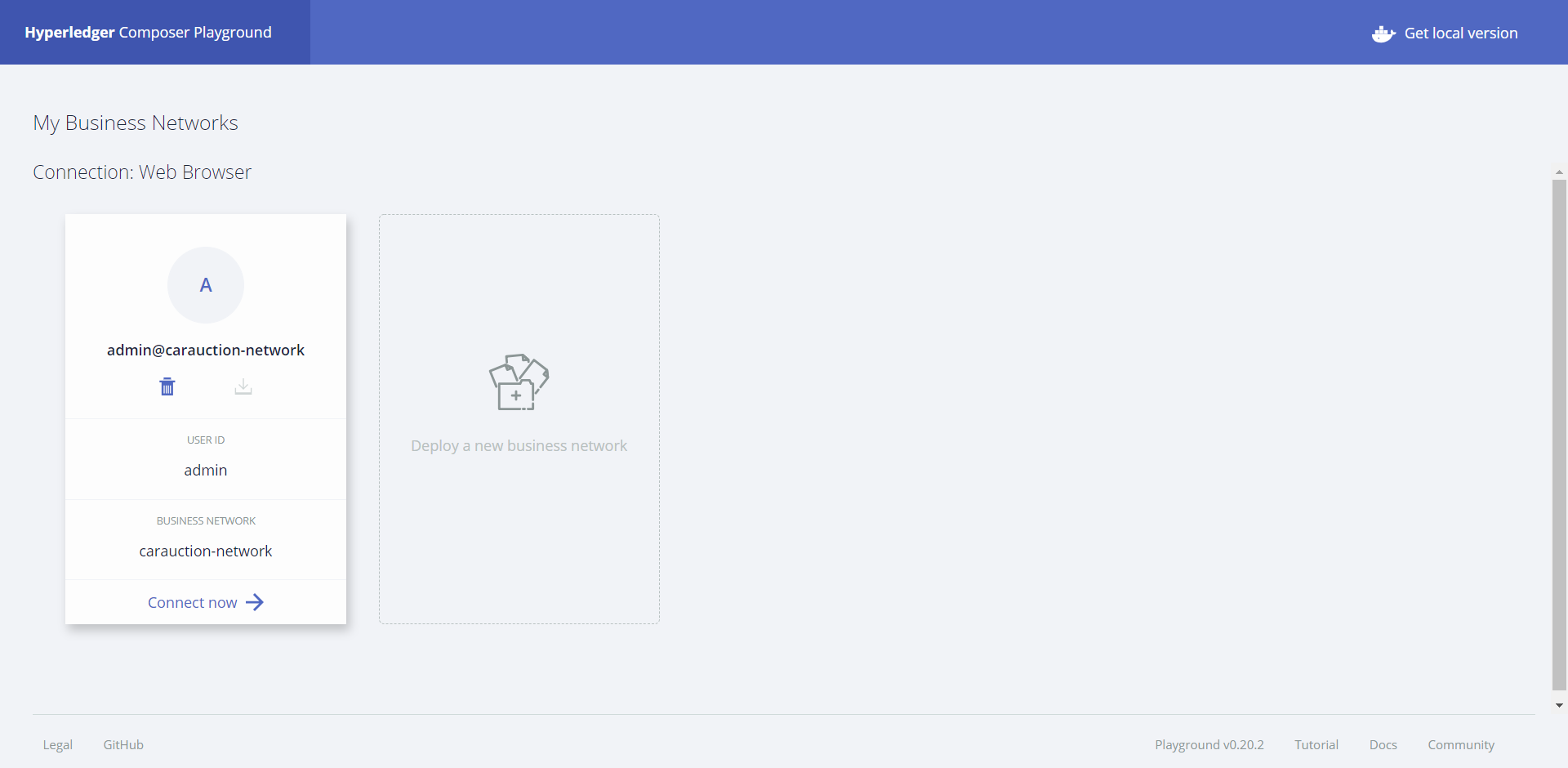
We can click on Connect Now and start making transactions such as creating participants and vehicles
Creating Transactions
Create some members by navigating to the Test Section (at the top) and then Members from the Menu and clicking on Create New Participant
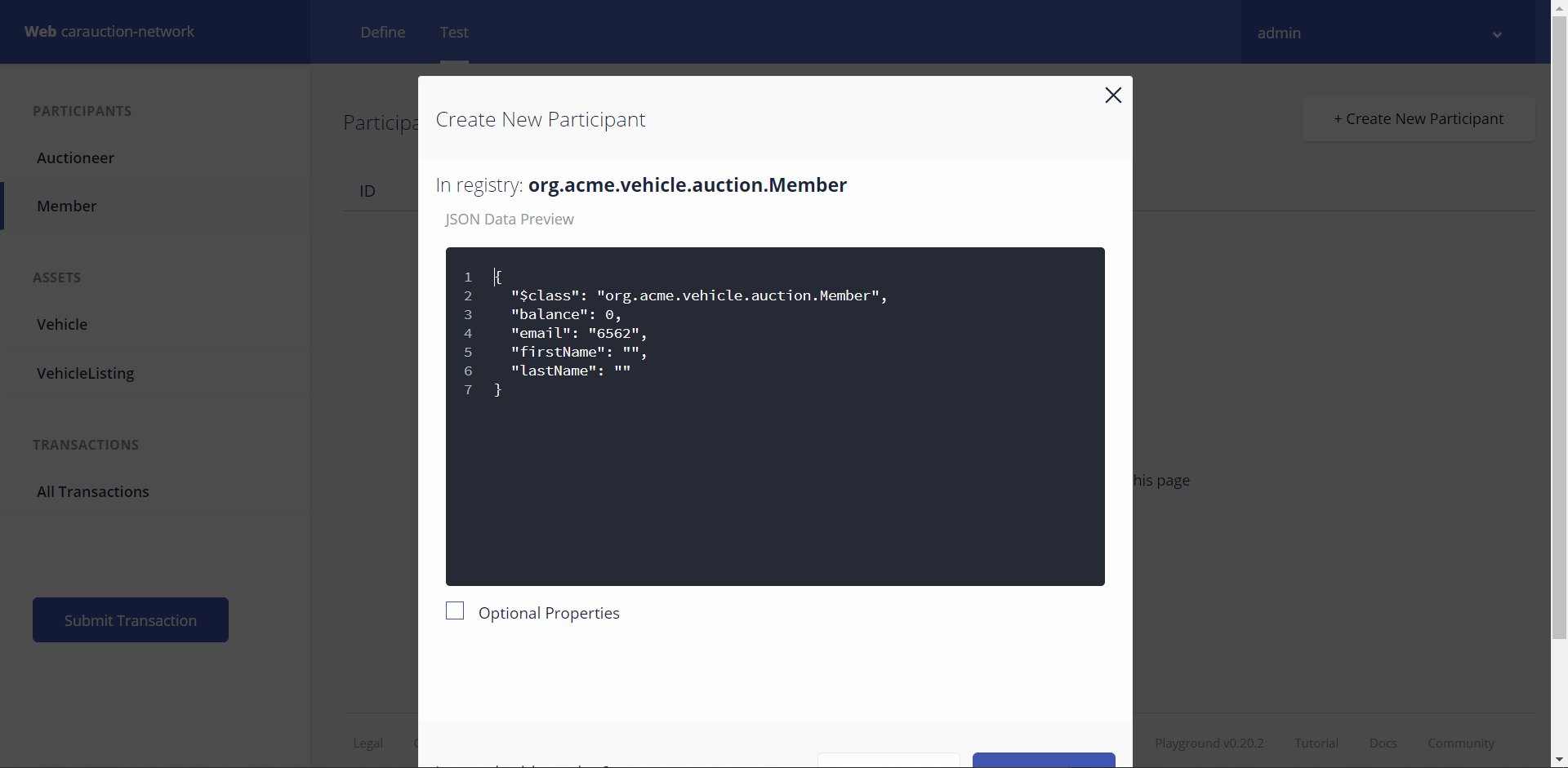
We can see our created Participants on the Member Screen
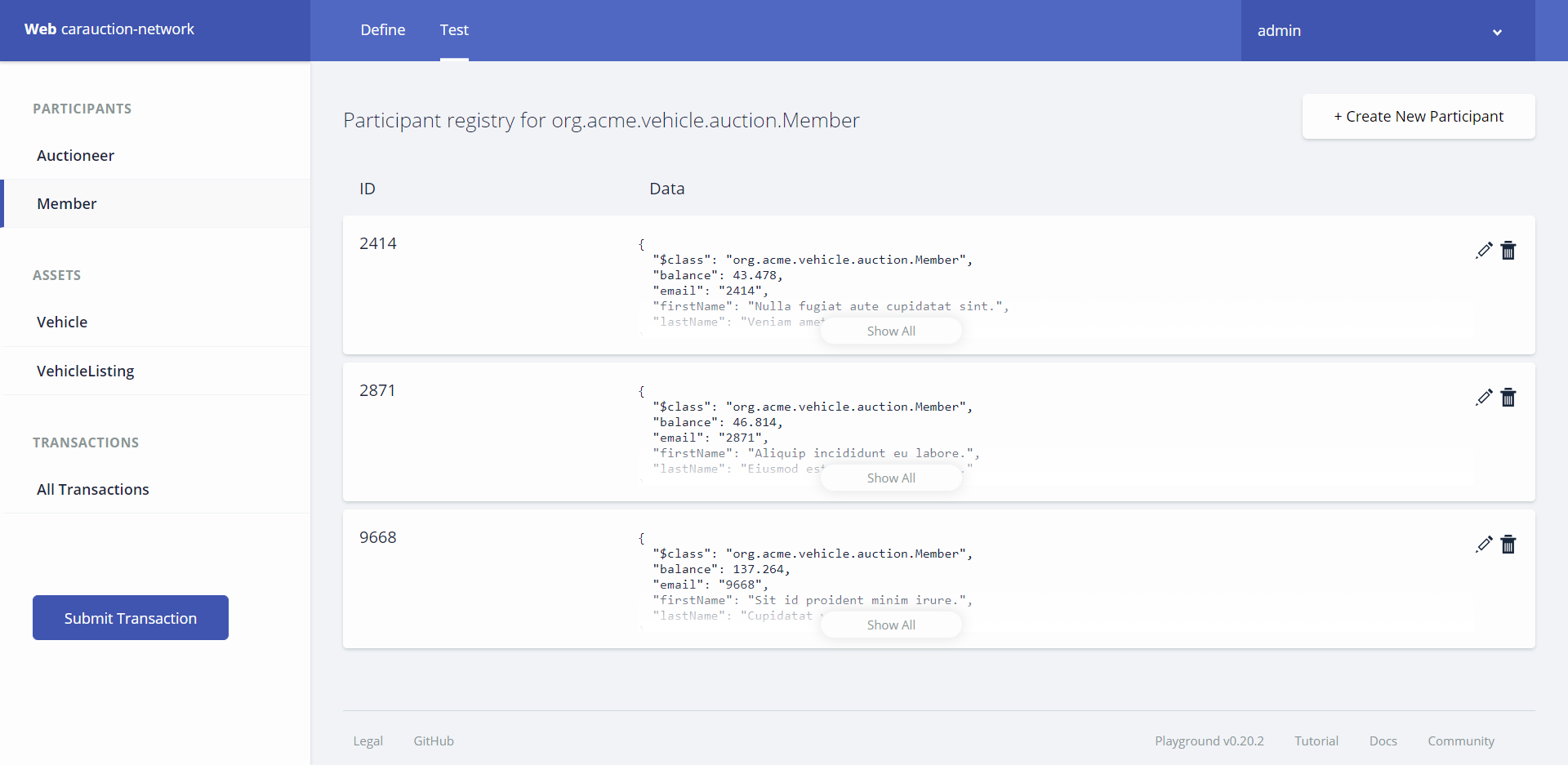
Once this has been done we can do the same for Vehicles and Vehicle Listings
We can look at the transactions made from the All Transactions page
.png)
Explore the Definitions
Head over to the editor screen and you will be able to see the different configuration available in our blockchain
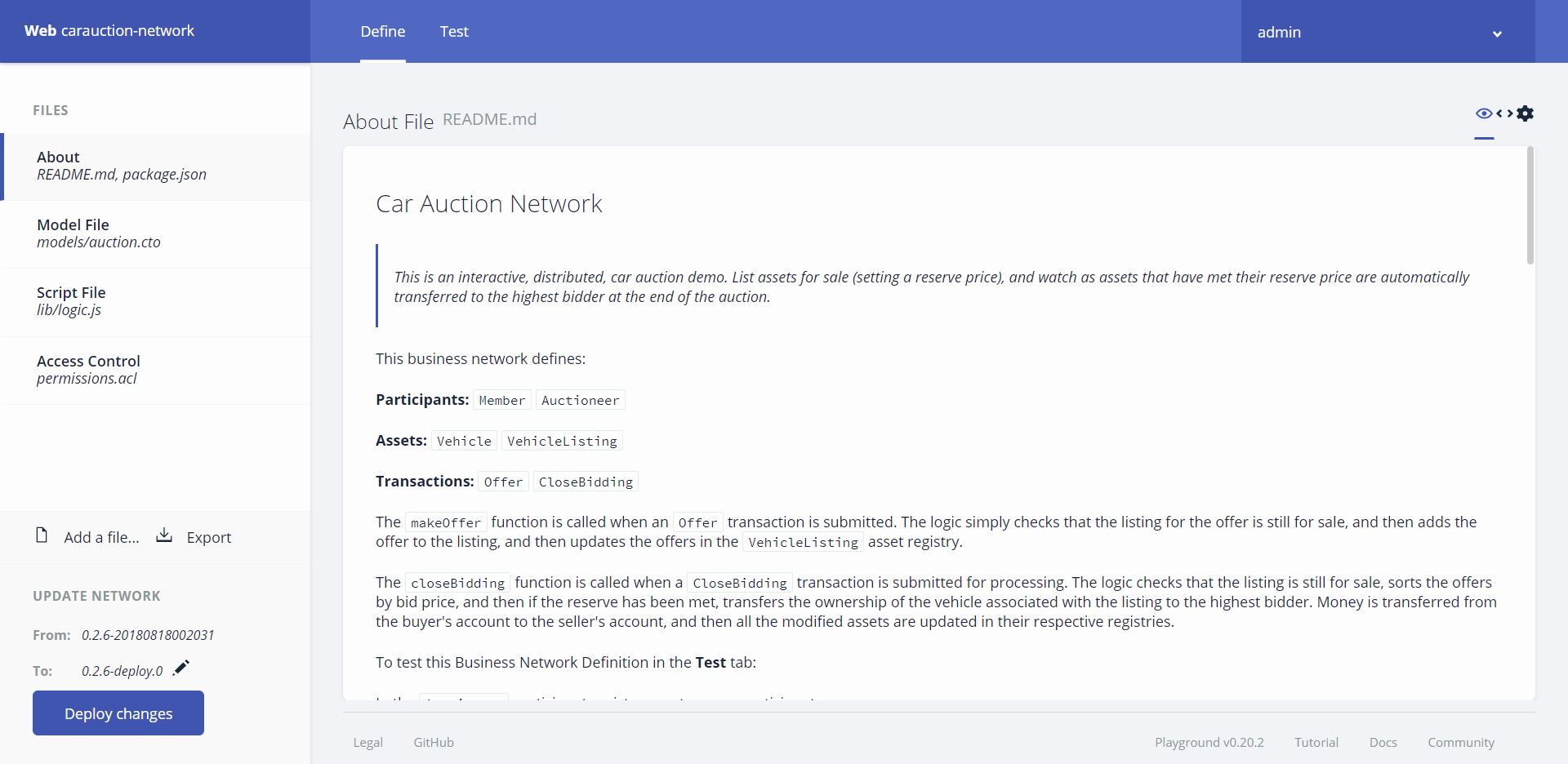
The different elements of our blockchain are defined with the following structures and rules
1namespace org.acme.vehicle.auction2
3asset Vehicle identified by vin {4 o String vin5 --> Member owner6}7
8enum ListingState {9
10 o FOR_SALE11 o RESERVE_NOT_MET12 o SOLD13}14
15asset VehicleListing identified by listingId {16 o String listingId17 o Double reservePrice18 o String description19 o ListingState state20 o Offer[] offers optional21 --> Vehicle vehicle22}23
24abstract participant User identified by email {25 o String email26 o String firstName27 o String lastName28}29
30participant Member extends User {31 o Double balance32}33
34participant Auctioneer extends User {35}36
37transaction Offer {38 o Double bidPrice39 --> VehicleListing listing40 --> Member member41}42
43transaction CloseBidding {44 --> VehicleListing listing45}1async function closeBidding(closeBidding) {2 // eslint-disable-line no-unused-vars3 const listing = closeBidding.listing4 if (listing.state !== 'FOR_SALE') {5 throw new Error('Listing is not FOR SALE')6 }7 // by default we mark the listing as RESERVE_NOT_MET8 listing.state = 'RESERVE_NOT_MET'9 let highestOffer = null10 let buyer = null11 let seller = null12 if (listing.offers && listing.offers.length > 0) {13 // sort the bids by bidPrice14 listing.offers.sort(function (a, b) {15 return b.bidPrice - a.bidPrice16 })17 highestOffer = listing.offers[0]18 if (highestOffer.bidPrice >= listing.reservePrice) {19 // mark the listing as SOLD20 listing.state = 'SOLD'21 buyer = highestOffer.member22 seller = listing.vehicle.owner23 // update the balance of the seller24 console.log('### seller balance before: ' + seller.balance)25 seller.balance += highestOffer.bidPrice26 console.log('### seller balance after: ' + seller.balance)27 // update the balance of the buyer28 console.log('### buyer balance before: ' + buyer.balance)29 buyer.balance -= highestOffer.bidPrice30 console.log('### buyer balance after: ' + buyer.balance)31 // transfer the vehicle to the buyer32 listing.vehicle.owner = buyer33 // clear the offers34 listing.offers = null35 }36 }37
38 if (highestOffer) {39 // save the vehicle40 const vehicleRegistry = await getAssetRegistry(41 'org.acme.vehicle.auction.Vehicle'42 )43 await vehicleRegistry.update(listing.vehicle)44 }45
46 // save the vehicle listing47 const vehicleListingRegistry = await getAssetRegistry(48 'org.acme.vehicle.auction.VehicleListing'49 )50 await vehicleListingRegistry.update(listing)51
52 if (listing.state === 'SOLD') {53 // save the buyer54 const userRegistry = await getParticipantRegistry(55 'org.acme.vehicle.auction.Member'56 )57 await userRegistry.updateAll([buyer, seller])58 }59}60
61/**62 * Make an Offer for a VehicleListing63 * @param {org.acme.vehicle.auction.Offer} offer - the offer64 * @transaction65 */66async function makeOffer(offer) {67 // eslint-disable-line no-unused-vars68 let listing = offer.listing69 if (listing.state !== 'FOR_SALE') {70 throw new Error('Listing is not FOR SALE')71 }72 if (!listing.offers) {73 listing.offers = []74 }75 listing.offers.push(offer)76
77 // save the vehicle listing78 const vehicleListingRegistry = await getAssetRegistry(79 'org.acme.vehicle.auction.VehicleListing'80 )81 await vehicleListingRegistry.update(listing)82}1rule Auctioneer {2 description: "Allow the auctioneer full access"3 participant: "org.acme.vehicle.auction.Auctioneer"4 operation: ALL5 resource: "org.acme.vehicle.auction.*"6 action: ALLOW7}8
9rule Member {10 description: "Allow the member read access"11 participant: "org.acme.vehicle.auction.Member"12 operation: READ13 resource: "org.acme.vehicle.auction.*"14 action: ALLOW15}16
17rule VehicleOwner {18 description: "Allow the owner of a vehicle total access"19 participant(m): "org.acme.vehicle.auction.Member"20 operation: ALL21 resource(v): "org.acme.vehicle.auction.Vehicle"22 condition: (v.owner.getIdentifier() == m.getIdentifier())23 action: ALLOW24}25
26rule VehicleListingOwner {27 description: "Allow the owner of a vehicle total access to their vehicle listing"28 participant(m): "org.acme.vehicle.auction.Member"29 operation: ALL30 resource(v): "org.acme.vehicle.auction.VehicleListing"31 condition: (v.vehicle.owner.getIdentifier() == m.getIdentifier())32 action: ALLOW33}34
35rule SystemACL {36 description: "System ACL to permit all access"37 participant: "org.hyperledger.composer.system.Participant"38 operation: ALL39 resource: "org.hyperledger.composer.system.**"40 action: ALLOW41}42
43rule NetworkAdminUser {44 description: "Grant business network administrators full access to user resources"45 participant: "org.hyperledger.composer.system.NetworkAdmin"46 operation: ALL47 resource: "**"48 action: ALLOW49}50
51rule NetworkAdminSystem {52 description: "Grant business network administrators full access to system resources"53 participant: "org.hyperledger.composer.system.NetworkAdmin"54 operation: ALL55 resource: "org.hyperledger.composer.system.**"56 action: ALLOW57}